Treating Ebola: progress and ethics
When there are only two doses of Ebola treatment available and thousands are in need, who gets them? Plummer and colleagues describe advances in countermeasures against Ebola and the ethical issues these therapies raise. See Commentary, page 1129
Metformin and TSH levels
Metformin monotherapy, compared with sulfonylurea monotherapy, was associated with an increased incidence of low levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) among patients receiving treatment for hypothyroidism. The association was not seen among euthyroid patients. The clinical consequences of this effect warrant further assessment, say the authors. See Research, page 1138

Care coordination for frequent users
Improving coordination of medical care can reduce hospital admissions among frequent users of health care services and reduce emergency department visits by frequent users 65 years and older. The authors of this systematic review suggest that some strategies, such as team changes, case management and promotion of self-management, are more effective than other quality improvement strategies. See Research, page E568
Older adults with chronic medical conditions benefit most from quality improvement strategies that involve coordinated efforts aimed at reducing hospital admissions, but issues of generalizability remain. See Commentary, page 1125

Long-term macrolides for COPD
Macrolide antibiotics have a well-defined role in treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) exacerbations, but there is renewed interest in long-term prophylactic use of macrolides in COPD. Parameswaran and Sethi review the immunomodulatory and antimicrobial actions of macrolides and discuss the evidence for potential benefits and harms. See Review, page 1148
Juurlink argues that conflicting evidence from recent studies about a possible association between azithromycin and cardiovascular death likely reflects a confounding effect of infection rather than a direct drug effect. See Commentary, page 1127

Dealing with missing data in trials
The results of randomized controlled trials can be biased, despite using an intention-to-treat analysis, if outcome data are missing in a selective manner and simple analyses are used, based only on participants with complete data. Groenwold and colleagues discuss how to report and analyze data from these trials so as to minimize bias in the results. See Analysis, page 1153
Acute pericarditis
A 28-year-old man presents to the emergency department with chest pain. His physician suspects acute pericarditis. Kennedy and Singh address questions around the diagnosis and management of acute pericarditis. See Decisions, page 1161
Two-stage hepatectomy
Patients with advanced liver tumours from metastatic colorectal cancer are often considered for palliative care. A new procedure may offer an option for surgical treatment intended to cure. Further study is required before this technique can be widely recommended. See Innovations, page 1163
Dermoscopy
Dermoscopy can be useful for primary care physicians in the diagnosis of melanoma and reduction of unnecessary biopsies of benign skin lesions, say Marchetti and Marghoob. See Five things to know about …, page 1167
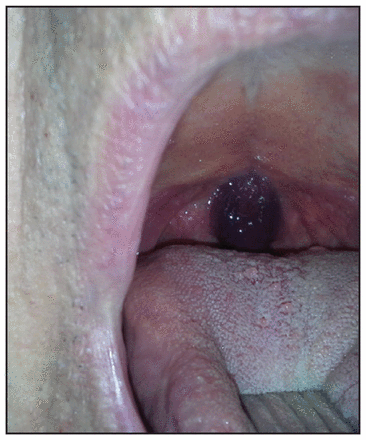
Spontaneous uvula hematoma
An 81-year-old man receiving dual antiplatelet therapy suddenly had a choking sensation after eating dinner. In the emergency department, spontaneous uvula hematoma, an unusual manifestation of bleeding, was diagnosed. Kounis and Davlouros discuss the risks of bleeding with dual antiplatelet therapy. See Clinical images, page 1168