Healthier hearts in family members
A heart-health intervention aimed at family members of patients with coronary artery disease improved measures of obesity and self-reported physical activity, and fruit and vegetable consumption, but did not improve the ratio of total cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol. Reid and colleagues randomly assigned 211 family members to an intervention that included feedback about risk factors and creating action plans for risk reduction. These findings suggest an opportunity to improve the cardiovascular health of family members, who may be at higher risk of heart disease. See Research, page 23
Home diagnosis of sleep apnea possible
Image courtesy of © 2013 Thinkstock
Portable devices used at home offer similar levels of diagnostic accuracy to sleep laboratory testing for diagnosing obstructive sleep apnea. This finding is based on a systematic review of 59 studies involving 5026 patients. Safe and convenient, portable devices confirm obstructive sleep apnea in patients with a high likelihood of the condition. See Research, page E25
Large trial for hip surgery now warranted
Performing surgery as soon as possible after a hip fracture shows promise and should be tested in a large randomized controlled trial. Buse and colleagues carried out a pilot trial involving 60 patients with a hip fracture to test the feasibility of conducting a larger trial of accelerated versus standard surgery. The results are encouraging, and the authors plan to start a large trial next year. See Research, page E52
Neuromodulation for major depressive disorder
Major depressive disorder fails to remit even after treatment with multiple drugs in approximately 40% of patients. Neuromodulation therapies are available that can effectively treat depression when pharmacotherapy has been ineffective. Lipsman and colleagues review the established role of electroconvulsive therapy and describe the emerging role of innovative therapies arising from technological advances, including transcranial magnetic stimulation and deep brain stimulation. See Review, page 33
Dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry in obesity

Two patients with a body mass index (BMI) ≥ 40 underwent the same type of bariatric surgery. After 1 year, both had achieved similar reductions in BMI and other anthropometric measures. However, their long-term outcomes may be quite different. Dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry showed a dramatic difference in body fat distribution between the two patients. See Practice, page 48
Gender dysphoria in a 39-year-old man
A patient presents to his family physician requesting estrogen. He explains that he has “felt more like a girl” since his early teen years and states that he can no longer tolerate living this way. Should he be given a prescription for estrogen at this visit? Does he require referral, and if so, to whom? What issues should be covered in this initial appointment? See Practice, page 49
Investigating venous thrombosis
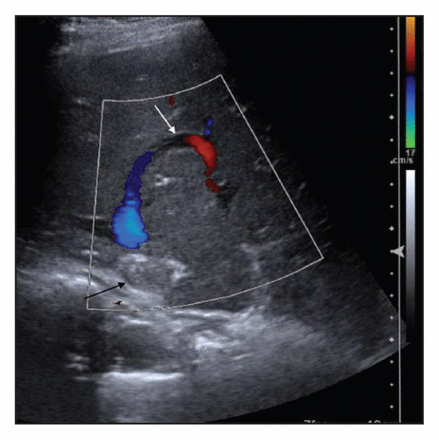
An otherwise healthy 35-year-old man presented with an almost occlusive thrombosis of his inferior vena cava. After extensive investigation, he was found to have essential thrombocythemia associated with a JAK2 mutation. Because ruling out causes of provoked venous thromboembolism requires a thorough history, examination and basic laboratory investigations, not all patients should undergo a battery of screening tests to look for hereditary causes of thrombophilia. See Practice, page 51
Postthrombotic syndrome
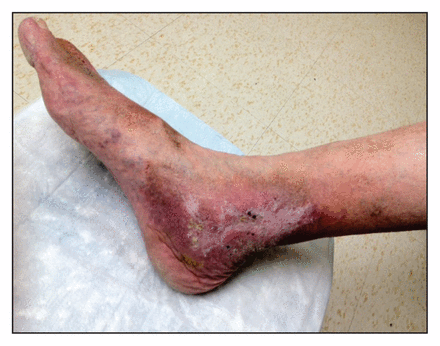
More than 50% of people with deep vein thrombosis (DVT) may subsequently have postthrombotic syndrome, a chronic but preventable condition that leads to limb pain, swelling, skin discolouration and ulceration. Preventive measures include using compression stockings and low–molecular-weight heparin (rather than oral anticoagulants) for at least 3 months after the diagnosis of DVT, say Kayssi and Roche-Nagle. See Practice, page 62