Abstract
OBJECTIVE: To investigate whether C-reactive protein (CRP) concentrations are influenced by body composition, insulin resistance, and body fat distribution in healthy women.
DESIGN: Cross-sectional study of CRP plasma levels in adult women.
SUBJECTS: A total of 201 apparently healthy normal weight, overweight, and obese women, aged 18–60 y.
MEASUREMENTS: CRP plasma levels, several fatness and body fat distribution parameters (by bioimpedance analysis and anthropometry), and insulin resistance (HOMAIR), as calculated by homeostatic model assessment.
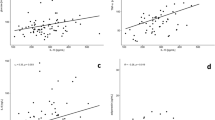
RESULTS: CRP was positively correlated with age, body mass index (BMI), waist, fasting glucose and insulin, HOMAIR, fat-free mass (FFM) and fat mass (FM). After multivariate analyses, age, HOMAIR, waist and FM maintained their independent association with CRP.
CONCLUSION: Our study has shown an independent relationship of central fat accumulation and insulin resistance with CRP plasma levels, thus suggesting that mild, chronic inflammation may be a further component of the metabolic syndrome and a mediator of the atherogenic profile of this syndrome.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pepys MB . The acute-phase response and C-reactive protein. In: Weatherall DJ, Ledingham JGG, Warrell DA (eds). Oxford textbook of medicine, 2nd edn Oxford University Press: Oxford 1995 pp 1527–1533.
Ridker PM, Buring JE, Shih J, Matias M, Hennekens CH . Prospective study of C-reactive protein and the risk of future cardiovascular events among apparently healthy women Circulation 1998 98: 731–733.
Ridker PM, Cushman M, Stampfer MJ, Tracy RP, Hennekens CH . Plasma concentration of C-reactive protein and the risk of developing peripheral vascular disease Circulation 1998 97: 425–428.
Koenig W, Sund M, Frohlich M, Fischer HG, Lowell H, Doring A, Hutchinson WL, Pepys MB . C-reactive protein, a sensitive marker of inflammation, predicts future risk of coronary heart disease in initially healthy middle-aged men Circulation 1999 99: 237–242.
Pepys MB, Rowe IF, Baltz ML . C-reactive protein: binding to lipids and lipoproteins Int Rev Exp Pathol 1985 27: 83–111.
Volanakis JE . Complement activation by C-reactive protein complexes Ann NY Acad Sci 1982 389: 235–250.
Cermak J, Key NS, Bach RR, Balla J, Jacob HS, Vercellotti GM . C-reactive protein induces human peripheral blood monocytes to synthesize tissue factor Blood 1993 82: 513–520.
Rohde LEP, Hennekens CH, Ridker PM . Survey of C-reactive protein and cardiovascular risk factors in apparently healthy men Am J Cardiol 1999 84: 1018–1022.
Visser M, Bouter LM, McQuillan GM, Wener MH, Harris TB . Elevated C-reactive protein levels in overweight and obese adults JAMA 1999 282: 2131–2135.
Hotamisligil GS, Arner P, Caro JF, Atkinson RL, Spiegelman BM . Increased adipose tissue expression of tumor necrosis factor-α in human obesity and insulin resistance J Clin Invest 1995 95: 2409–2415.
Purhoit A, Ghilchik MW, Duncan L, Wang DY, Singh A, Walker MM, Reed MJ . Aromatase activity and interleukin-6 production by normal and malignant breast tissue J Clin Endocrinol 1995 9: 61–72.
Baumann H, Gauldie J . The acute-phase response Immunol Today 1994 25: 74–80.
Papanicolaou DA, Wilder RL, Manolagas SC, Chrousos GP . The pathophysiologic roles of interleukin-6 in human disease Ann Intern Med 1998 128: 127–137.
Yudkin JS, Stehouwer CDA, Emeis JJ, Coppack SW . C-reactive protein in healthy subjects: associations with obesity, insulin resistance, and endothelial dysfunction Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 1999 19: 972–978.
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC . Homeostatic model assessment: insulin resistance and β-cell function from fasting glucose and insulin concentrations in man Diabetologia 1985 28: 412–419.
Report of the Expert Committee on the Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus . Diabetes Care 1997 20: 1183–1197.
Heitmann BL . Prediction of body water and fat in adult Danes from measurement of electrical impedance. A validation study. Int J Obes 1990 14: 789–802.
Ridker PM, Hennekens CH, Buring JE, Rifai N . C-reactive protein and other markers of inflammation in the prediction of cardiovascular disease in women New Engl J Med 2000 342: 836–843.
Pi-Sunyer FX . Health implications of obesity Am J Clin Nutr 1991 53: 1595S–1603S.
Rimm EB, Stampfer MJ, Giovannucci E, Ascherio A, Spiegelman D, Colditz GA, Willett WC . Body size and fat distribution as predictors of coronary heart disease among middle-aged and older US men Am J Epidemiol 1995 141: 1117–1127.
Folsom AR, Stevens J, Schreiner PJ, McGovern PG . Body mass index, waist/hip ratio, and coronary heart disease incidence in African-Americans and whites Am J Epidemiol 1998 148: 1187–1194.
Gaudet D, Vohl MC, Perron P, Tremblay G, Gagné C, Lesiege D, Bergeron J, Moorjani S, Després JP . Relationship of abdominal obesity and hyperinsulinemia to angiographically assessed coronary artery disease in men with known mutations in the LDL receptor gene Circulation 1998 97: 871–877.
Després JP . The insulin resistance-dyslipidemic syndrome of visceral obesity: effect on patients' risk Obes Res 1998 6: (Suppl 1): 8S–17S.
Imbeault P, Lemieux S, Preud'homme D, Tremblay A, Nadeau A, Després JP, Mauriege P . Relationship of visceral adipose tissue to metabolic risk factors for coronary heart disease: is there a contribution of subcutaneous fat cell hypertrophy? Metabolism 1999 48: 355–362.
Reeder B, Bouchard C . Obesity and cardiovascular diseases Can J Cardiol 1999 15: (Suppl G): 69G–72G.
Mendall MA, Patel P, Ballam L, Strachan D, Northfield TC . C-reactive protein and its relation to cardiovascular risk factors Br Med J 1996 312: 1061–1065.
Tracy RP, Lemaitre RN, Psaty BM, lves DG, Evans RW, Cushman M, Meilahn EN, Kuller LH . Relationship of C-reactive protein to risk of cardiovascular disease in the elderly Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 1997 17: 1121–1127.
Pratley RE, Wilson C, Bogardus C . Relation of the white blood cell count to obesity and insulin resistance: effect of race and gender Obes Res 1995 3: 563–571.
Fried SK, Bunkin DA, Greenberg AS . Omental and subcutaneous adipose tissues of obese subjects release interleukin-6 J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1998 83: 847–850.
Hotamisligil GS, Peraldi P, Budavari A, Ellis R, White MF, Spiegelman BM . IRS-1-mediated inhibition of insulin receptor tyrosine kinase activity in TNF-α- and obesity-induced insulin resistance Science 1996 271: 665–668.
Hotamisligil GS . The role of TNF alpha and TNF receptors in obesity and insulin resistance J Intern Med 1999 245: 621–625.
Hotamisligil GS . Mechanisms of TNF-alpha-induced insulin resistance Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 1999 107: 119–125.
Festa A, D'Agostino R Jr, Howard G, Mykkanen L, Tracy RP, Haffner SM . Chronic subclinical inflammation as part of insulin resistance syndrome: the insulin resistance atherosclerosis study Circulation 2000 102: 42–47.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pannacciulli, N., Cantatore, F., Minenna, A. et al. C-reactive protein is independently associated with total body fat, central fat, and insulin resistance in adult women. Int J Obes 25, 1416–1420 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801719
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801719
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Causal association of obesity with epigenetic aging and telomere length: a bidirectional mendelian randomization study
Lipids in Health and Disease (2024)
-
Elevated C-reactive protein and complement C3 levels are associated with preterm birth: a nested case–control study in Chinese women
BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth (2020)
-
Stability and reproducibility of proteomic profiles measured with an aptamer-based platform
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Abdominal obesity and hip fracture: results from the Nurses’ Health Study and the Health Professionals Follow-up Study
Osteoporosis International (2016)
-
Interleukin-6 is a better metabolic biomarker than interleukin-18 in young healthy adults
Journal of Physiology and Biochemistry (2015)