Abstract
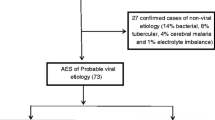
Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) is estimated to cause 30–50,000 cases of encephalitis every year. The disease occurs mainly in rural Asia and is transmitted to humans from birds and pigs by mosquitoes of the genus Culex. JE is diagnosed with antibody testing of the serum and CSF, but this is not available in many hospitals. Neuroimaging abnormalities, particularly thalamic hypodensity on computed tomography (CT) and hyperintensity on T2 weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) have been described in case studies, but their usefulness for diagnosing JE is not known. We have therefore evaluated the usefulness of neuroimaging (CT and MRI) for the diagnosis of JE. The findings of thalamic lesions were compared with the final serological diagnosis in a cohort of 75 patients (children and adults) with suspected CNS infections in Southern Vietnam, a JEV endemic area. Thalamic lesions on CT and/or MRI combined had sensitivity 23% (95% confidence interval 12.9–33.1%), specificity 100%, positive predictive value 100% and negative predictive value 42.1% (95% confidence interval 30.2–53.8%) for a diagnosis of JE in this cohort. Over time, the thalamic lesions resolved in some patients. One patient showed disappearance of lesions on CT followed by reappearance of the lesions some time later, known as the fogging effect. In this setting, the presence of thalamic abnormalities suggested the diagnosis of JE, but their absence did not exclude it.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
World Health Organisation (2006) Japanese encephalitis vaccines. Wkly Epidemiol Rec 81(34/35):331–340
Becker H, Desch H, Hacker H, Pencz A (1979) CT fogging effect with ischemic cerebral infarcts. Neuroradiology 18:185–192. doi:10.1007/BF00345723
Bosanko CM, Gilroy J, Wang AM, Sanders W, Dulai M, Wilson J, Blum K (2003) West Nile virus encephalitis involving the substantia nigra: neuroimaging and pathologic findings with literature review. Arch Neurol 60:1448–1452. doi:10.1001/archneur.60.10.1448
Burke DS, Nisalak A, Ussery MA (1982) Antibody capture immunoassay detection of Japanese encephalitis virus immunoglobulin m and g antibodies in cerebrospinal fluid. J Clin Microbiol 16:1034–1042
Burke DS, Nisalak A, Ussery MA, Laorakpongse T, Chantavibul S (1985) Kinetics of IgM and IgG responses to Japanese encephalitis virus in human serum and cerebrospinal fluid. J Infect Dis 151:1093–1099
Deresiewicz RL, Thaler SJ, Hsu L, Zamani AA (1997) Clinical and neuroradiographic manifestations of eastern equine encephalitis. N Engl J Med 336:1867–1874. doi:10.1056/NEJM199706263362604
Desai A, Shankar SK, Ravi V, Chandramuki A, Gourie-Devi M (1995) Japanese encephalitis virus antigen in the human brain and its topographic distribution. Acta Neuropathol 89:368–373. doi:10.1007/BF00309631
Edgren DC, Palladino VS, Arnold A (1958) Japanese B and mumps encephalitis: a clinicopathological report of simultaneous outbreaks on the island of Guam. Am J Trop Med Hyg 7:471–480
Einsiedel L, Kat E, Ravindran J, Slavotinek J, Gordon DL (2003) MR findings in Murray Valley encephalitis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1379–1382
German AC, Myint KS, Mai NT, Pomeroy I, Phu NH, Tzartos J, Winter P, Collett J, Farrar J, Barrett A, Kipar A, Esiri MM, Solomon T (2006) A preliminary neuropathological study of Japanese encephalitis in humans and a mouse model. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 100:1135–1145. doi:10.1016/j.trstmh.2006.02.008
Handique SK, Das RR, Barman K, Medhi N, Saharia B, Saikia P, Ahmed SA (2006) Temporal lobe involvement in Japanese encephalitis: problems in differential diagnosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27:1027–1031
Innis BL, Nisalak A, Nimmannitya S, Kusalerdchariya S, Chongswasdi V, Suntayakorn S, Puttisri P, Hoke CH (1989) An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to characterize dengue infections where dengue and Japanese encephalitis co-circulate. Am J Trop Med Hyg 40:418–427
Johnson RT, Burke DS, Elwell M, Leake CJ, Nisalak A, Hoke CH, Lorsomrudee W (1985) Japanese encephalitis: immunocytochemical studies of viral antigen and inflammatory cells in fatal cases. Ann Neurol 18:567–573. doi:10.1002/ana.410180510
Kalita J, Misra UK (2000) Comparison of CT scan and MRI findings in the diagnosis of Japanese encephalitis. J Neurol Sci 174:3–8. doi:10.1016/S0022-510X(99)00318-4
Kalita J, Misra UK, Pandey S, Dhole TN (2003) A comparison of clinical and radiological findings in adults and children with Japanese encephalitis. Arch Neurol 60:1760–1764. doi:10.1001/archneur.60.12.1760
Kamble R, Peruvamba JN, Kovoor J, Ravishankar S, Kolar BS (2007) Bilateral thalamic involvement in dengue infection. Neurol India 55:418–419. doi:10.4103/0028-3886.37103
Kimura K, Dosaka A, Hashimoto Y, Yasunaga T, Uchino M, Ando M (1997) Single-photon emission CT findings in acute Japanese encephalitis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 18:465–469
Kumar S, Misra UK, Kalita J, Salwani V, Gupta RK, Gujral R (1997) MRI in Japanese encephalitis. Neuroradiology 39:180–184. doi:10.1007/s002340050388
Lorenzl S, Pfister HW, Padovan C, Yousry T (1996) MRI abnormalities in tick-borne encephalitis. Lancet 347:698–699. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(96)91256-8
Marjelund S, Tikkakoski T, Tuisku S, Raisanen S (2004) Magnetic resonance imaging findings and outcome in severe tick-borne encephalitis. Report of four cases and review of the literature. Acta Radiol 45:88–94. doi:10.1080/02841850410003356
Misra UK, Kalita J (1997) Movement disorders in Japanese encephalitis. J Neurol 244:299–303. doi:10.1007/s004150050090
Misra UK, Kalita J (2001) Seizures in Japanese encephalitis. J Neurol Sci 190:57–60. doi:10.1016/S0022-510X(01)00589-5
Misra UK, Kalita J, Goel D, Mathur A (2003) Clinical, radiological and neurophysiological spectrum of JEV encephalitis and other non-specific encephalitis during post-monsoon period in India. Neurol India 51:55–59
Misra UK, Kalita J, Jain SK, Mathur A (1994) Radiological and neurophysiological changes in Japanese encephalitis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 57:1484–1487. doi:10.1136/jnnp.57.12.1484
Miyake M (1964) The pathology of Japanese encephalitis. A review. Bull World Health Organ 30:153–160
Molyneux ME, Taylor TE, Wirima JJ, Borgstein A (1989) Clinical features and prognostic indicators in paediatric cerebral malaria: a study of 131 comatose Malawian children. Q J Med 71:441–459
Nakashima A, Horichi Y, Takagi Y, Miyamoto S, Takashima S, Inoue H (1999) A case of Japanese encephalitis: CT and MRI findings in acute and convalescent stages. Radiat Med 17:369–371
Ooi MH, Lewthwaite P, Lai BF, Mohan A, Clear D, Lim L, Krishnan S, Preston T, Chieng CH, Tio PH, Wong SC, Cardosa J, Solomon T (2008) The epidemiology, clinical features, and long-term prognosis of Japanese encephalitis in Central Sarawak, Malaysia, 1997–2005. Clin Infect Dis 47(4):458–468
Pradhan S, Pandey N, Shashank S, Gupta RK, Mathur A (1999) Parkinsonism due to predominant involvement of substantia nigra in Japanese encephalitis. Neurology 53:1781–1786
Sejvar JJ, Haddad MB, Tierney BC, Campbell GL, Marfin AA, Van Gerpen JA, Fleischauer A, Leis AA, Stokic DS, Petersen LR (2003) Neurologic manifestations and outcome of West Nile virus infection. JAMA 290:511–515. doi:10.1001/jama.290.4.511
Shoji H, Hiraki Y, Kuwasaki N, Toyomasu T, Kaji M, Okudera T (1989) Japanese encephalitis in the Kurume region of Japan: CT and MRI findings. J Neurol 236:255–259. doi:10.1007/BF00314452
Shoji H, Kida H, Hino H, Matsuura S, Kojima K, Abe T, Utsunomiya H, Okada Y, Nakamura Y, Okudera T (1994) Magnetic resonance imaging findings in Japanese encephalitis. White matter lesions. J Neuroimaging 4:206–211
Shoji H, Murakami T, Murai I, Kida H, Sato Y, Kojima K, Abe T, Okudera T (1990) A follow-up study by CT and MRI in 3 cases of Japanese encephalitis. Neuroradiology 32:215–219. doi:10.1007/BF00589115
Skriver EB, Olsen TS (1981) Transient disappearance of cerebral infarcts on CT scan, the so-called fogging effect. Neuroradiology 22:61–65. doi:10.1007/BF00344775
Solomon T, Dung NM, Kneen R, le Thao TT, Gainsborough M, Nisalak A, Day NP, Kirkham FJ, Vaughn DW, Smith S, White NJ (2002) Seizures and raised intracranial pressure in Vietnamese patients with Japanese encephalitis. Brain 125:1084–1093. doi:10.1093/brain/awf116
Solomon T, Dung NM, Vaughn DW, Kneen R, Thao LT, Raengsakulrach B, Loan HT, Day NP, Farrar J, Myint KS, Warrell MJ, James WS, Nisalak A, White NJ (2000) Neurological manifestations of dengue infection. Lancet 355:1053–1059. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(00)02036-5
Solomon T, Dung NM, Wills B, Kneen R, Gainsborough M, Diet TV, Thuy TT, Loan HT, Khanh VC, Vaughn DW, White NJ, Farrar JJ (2003) Interferon alfa-2a in Japanese encephalitis: a randomised double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 361:821–826. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(03)12709-2
Solomon T, Fisher AF, Beasley DW, Mandava P, Granwehr BP, Langsjoen H, Travassos Da Rosa AP, Barrett AD, Tesh RB (2003) Natural and nosocomial infection in a patient with West Nile encephalitis and extrapyramidal movement disorders. Clin Infect Dis 36:E140–E145. doi:10.1086/374936
Solomon T, Kneen R, Dung NM, Khanh VC, Thuy TT, Ha DQ, Day NP, Nisalak A, Vaughn DW, White NJ (1998) Poliomyelitis-like illness due to Japanese encephalitis virus. Lancet 351:1094–1097. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(97)07509-0
Solomon T, Thao LT, Dung NM, Kneen R, Hung NT, Nisalak A, Vaughn DW, Farrar J, Hien TT, White NJ, Cardosa MJ (1998) Rapid diagnosis of Japanese encephalitis by using an immunoglobulin M dot enzyme immunoassay. J Clin Microbiol 36:2030–2034
Teasdale G, Jennett B (1974) Assessment of coma and impaired consciousness. A practical scale. Lancet 2:81–84. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(74)91639-0
Toyomasu T, Nakashima K, Matsumoto T, Shida K (1982) CT findings in a case of Japanese encephalitis. Clin Neurol (Tokyo) 22:891–895
Verity CM, Butler NR, Golding J (1985) Febrile convulsions in a national cohort followed up from birth. I–Prevalence and recurrence in the first five years of life. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 290:1307–1310
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the director and staff of the Centre for Tropical Diseases for their support, in particular Tran Tinh Hien and the doctors and nurses of the adult and paediatric intensive care units. David Vaughn and staff at AFRIMS, Bangkok gave diagnostic support, and Mani Putharan at the Walton Centre gave assistance with the images in this paper. This work was funded by the Wellcome Trust of Great Britain. TS is an MRC Senior Clinical Fellow.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dung, N.M., Turtle, L., Chong, W.K. et al. An evaluation of the usefulness of neuroimaging for the diagnosis of Japanese encephalitis. J Neurol 256, 2052–2060 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-009-5249-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-009-5249-5