Abstract
Introduction
The aim of this study was to evaluate the patterns of hypoglycemic encephalopathy on diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) and the relationship between the imaging patterns and clinical outcomes.
Methods
This retrospective study included 17 consecutive patients that had hypoglycemic encephalopathy with DWI abnormalities. The topographic distributions of the DWI abnormalities of the cortex, deep gray matter, and white matter structures were assessed. In addition, possible correlation between the patterns of brain injury on DWI and clinical outcomes was investigated.
Results
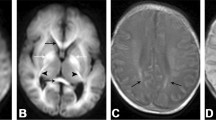
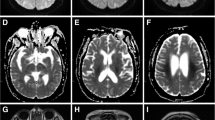
There were three patterns of DWI abnormalities: involvement of both gray and white matter (n = 8), selective involvement of gray matter (n = 4), and selective involvement of white matter (n = 5). There was no significant difference in the initial blood glucose levels among patients for each of the imaging patterns. Most patients (16/17) had bilateral symmetrical abnormalities. Among patients with bilateral symmetrical gray and/or white matter injuries, one had moderate to severe disability and 14 remained in a persistent vegetative state. The two patients with a focal unilateral white matter abnormality and a localized splenial abnormality recovered without neurological deficits.
Conclusion
The results of this study showed that white matter was more sensitive to hypoglycemia than previously thought and there was no specific association between the patterns of injury and clinical outcomes whether the cerebral cortex, deep gray matter, and/or white matter were affected. Diffuse and extensive injury observed on the DWI predicts a poor neurologic outcome in patients with hypoglycemic injuries.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Auer RN, Hugh J, Cosgrove E, Curry B (1989) Neuropathologic findings in three cases of profound hypoglycemia. Clin Neuropathol 8:63–68
Boeve BF, Bell DG, Noseworthy JH (1995) Bilateral temporal lobe MRI changes in uncomplicated hypoglycemic coma. Can J Neurol Sci 22:56–58
Fujioka M, Okuchi K, Hiramatsu KI, Sakaki T, Sakaguchi S, Ishii Y (1997) Specific changes in human brain after hypoglycemic injury. Stroke 28:584–587
Cordonnier C, Oppenheim C, Lamy C, Meder JF, Mas JL (2005) Serial diffusion and perfusion-weighted MR in transient hypoglycemia. Neurology 65:175
Aoki T, Sato T, Hasegawa K, Ishizaki R, Saiki M (2004) Reversible hyperintensity lesion on diffusion-weighted MRI in hypoglycemic coma. Neurology 63:392–393
Bottcher J, Kunze A, Kurrat C et al (2005) Localized reversible reduction of apparent diffusion coefficient in transient hypoglycemia-induced hemiparesis. Stroke 36:e20–e22
Albayram S, Ozer H, Gokdemir S et al (2006) Reversible reduction of apparent diffusion coefficient values in bilateral internal capsules in transient hypoglycemia-induced hemiparesis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27:1760–1762
Lo L, Tan AC, Umapathi T, Lim CC (2006) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging in early diagnosis and prognosis of hypoglycemia. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27:1222–1224
Maruya J, Endoh H, Watanabe H, Motoyama H, Abe H (2007) Rapid improvement of diffusion-weighted imaging abnormalities after glucose infusion in hypoglycaemic coma. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 78:102–103
Terakawa Y, Tsuyuguchi N, Nunomura K et al (2007) Reversible diffusion-weighted imaging changes in the splenium of the corpus callosum and internal capsule associated with hypoglycemia—case report. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 47:486–488
Kim JH, Choi JY, Koh SB, Lee Y (2007) Reversible splenial abnormality in hypoglycemic encephalopathy. Neuroradiology 49:217–222
Finelli PF (2001) Diffusion-weighted MR in hypoglycemic coma. Neurology 57:933
Yanagawa Y, Isoi N, Tokumaru AM, Sakamoto T, Okada Y (2006) Diffusion-weighted MRI predicts prognosis in severe hypoglycemic encephalopathy. J Clin Neurosci 13:696–699
Kalimo H, Olsson Y (1980) Effects of severe hypoglycemia on the human brain. Neuropathological case reports. Acta Neurol Scand 62:345–356
Dolinak D, Smith C, Graham DI (2000) Hypoglycaemia is a cause of axonal injury. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 26:448–453
de Courten-Myers GM, Xi G, Hwang JH et al (2000) Hypoglycemic brain injury: potentiation from respiratory depression and injury aggravation from hyperglycemic treatment overshoots. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 20:82–92
Pelligrino D, Almquist LO, Siesjo BK (1981) Effects of insulin-induced hypoglycemia on intracellular ph and impedance in the cerebral cortex of the rat. Brain Res 221:129–147
Hasegawa Y, Formato JE, Latour LL et al (1996) Severe transient hypoglycemia causes reversible change in the apparent diffusion coefficient of water. Stroke 27:1648–1655 discussion 1655–1656
Auer RN (1986) Progress review: hypoglycemic brain damage. Stroke 17:699–708
Paschen W, Bengtsson F, Rohn G, Bonnekoh P, Siesjo B, Hossmann KA (1991) Cerebral polyamine metabolism in reversible hypoglycemia of rat: relationship to energy metabolites and calcium. J Neurochem 57:204–215
Kawai K, Nitecka L, Ruetzler CA et al (1992) Global cerebral ischemia associated with cardiac arrest in the rat: I. Dynamics of early neuronal changes. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 12:238–249
Kiessling M, Xie Y, Kleihues P (1984) Regionally selective inhibition of cerebral protein synthesis in the rat during hypoglycemia and recovery. J Neurochem 43:1507–1514
Gallucci M, Limbucci N, Paonessa A, Caranci F (2007) Reversible focal splenial lesions. Neuroradiology 49:541–544
Kim JH, Koh SB (2007) Extensive white matter injury in hypoglycemic coma. Neurology 68:1074
Le Bihan D (2007) The ‘wet mind’: water and functional neuroimaging. Phys Med Biol 52:R57–R90
Hassel B, Boldingh KA, Narvesen C, Iversen EG, Skrede KK (2003) Glutamate transport, glutamine synthetase and phosphate-activated glutaminase in rat CNS white matter. A quantitative study. J Neurochem 87:230–237
Mori F, Nishie M, Houzen H, Yamaguchi J, Wakabayashi K (2006) Hypoglycemic encephalopathy with extensive lesions in the cerebral white matter. Neuropathology 26:147–152
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, JH., Kim, YJ., Yoo, WJ. et al. MR imaging of hypoglycemic encephalopathy: lesion distribution and prognosis prediction by diffusion-weighted imaging. Neuroradiology 51, 641–649 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-009-0544-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-009-0544-5