NEW! Listen to CMAJ editors discuss and comment on the content of this issue. Visit soundcloud.com/cmajpodcasts
Resident hours and patient outcomes

Work schedules incorporating shorter periods of continuous duty did not affect daytime sleepiness of residents or adverse events. This randomized trial did not detect any effect on the primary trial outcomes but did suggest more severe somatic symptoms among doctors allocated to longer periods of continuous duty. More precise quantification will require the conduct of larger randomized studies, suggest the authors. See Research, page 321
Resident duty-hour reform must be evidence-based. Maniatis stresses the importance of fully understanding the effects of resident scheduling systems on residents, faculty and patients, to ensure that altered rotas provide maximal benefit and minimal harms for all. See Commentary, page 309
Cognitive test for diverse populations
The RUDAS, a brief and freely available tool, compares well with standard tools assessing cognitive deficits, find Naqvi and colleagues in their meta-analysis. What’s more, it was developed for particular use among patients whose first language is not English, which makes it useful in settings where patient groups are diverse. See Research, page E169
Follow-up for patients with chest pain

Patients discharged after an emergency department visit for chest pain were less likely to be seen within 30 days by a primary care physician or cardiologist if they had known cardiac or cerebrovascular conditions, as well as certain other comorbidities. This observational study analyzed population health services data from Ontario on 56 767 patients over six years. The paradoxical finding that patients at higher risk for adverse events were less likely to receive follow-up calls for a better strategy to improve transition of care in this context, say the authors. See Research, page E160
Managing neonatal jaundice
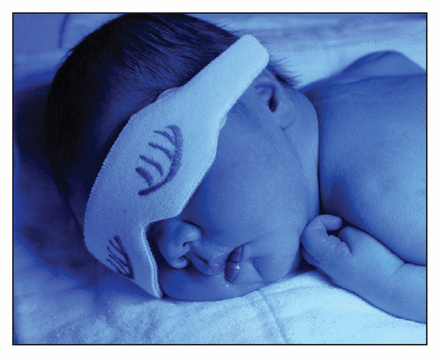
Kernicterus, or chronic bilirubin encephalopathy, still occurs in newborns in the developed world even though it is preventable. Combining the total serum bilirubin measurement with the infant’s gestational age provides an excellent prediction of hyperbilirubinemia risk. Follow-up of newborns discharged soon after birth is important. See Review, page 335
Nocturia
A 64-year-old man presents with a six-month history of frequent urination in the night. What is the cause of his symptoms? What investigations are required? Gill and Biyani review the evidence and share their approach to managing this problem. See Decisions, page 348
Atrial mass in molar pregnancy
A right atrial mass developed in a 23-year-old woman after she was treated for molar pregnancy. Is the mass metastatic disease from the molar pregnancy or is there another more likely diagnosis? Sharma and coauthors describe their approach to diagnosing and treating the patient’s condition. See What is your call?, page 350
Cannabinoid hyperemesis syndrome
When a regular cannabis user experiences cyclic vomiting relieved by taking numerous hot showers or baths, consider cannabinoid hyperemesis syndrome. An underrecognized clinical syndrome, it requires cessation of cannabis use for permanent remission, say King and Holmes. See Five things to know about …, page 355
Eruptive xanthomas in tattoos
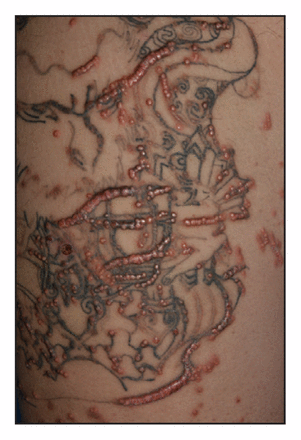
A 26-year-old man had papules following the lines of his 18-month-old tattoos. He was found to have hyperlipidemia and was given the diagnosis of eruptive xanthomas, associated with Koebner phenomenon. See Clinical images, page 356












Podcast