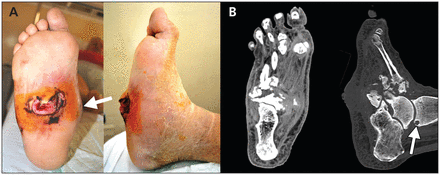
A 59-year-old man presented because of a swollen, numb and deformed right foot, with a 2-month history of a large plantar ulcer. He reported severe sensory loss in his feet and tingling in both legs, as well as difficulty putting on his shoes. He had been diagnosed with type 2 diabetes mellitus 15 years earlier, which had been poorly controlled recently. He also had severe peripheral neuropathy of 2 years’ duration. He had no history of trauma to the foot. On examination, he had a collapse of the arch of his right foot with a rocker bottom deformity and medial convexity (Figure 1A, arrow), along with a large neuropathic ulcer on the midplantar surface. Results of laboratory testing showed elevation of serum glucose at 9.9 (normal 4–8) mmol/L and hemoglobin A1C at 9.7% (normal 4%–6%), and were otherwise unremarkable; peripheral pulses were normal. Computed tomography of his right foot showed subchondral cysts (Figure 1B, arrow), fragmentation, disorganization and loss of normal architecture of the bones of the foot, consistent with Charcot foot.
(A) The right foot (plantar and lateral views) of a 59-year-old man with diabetic neuropathy showing collapse of the internal arch (arrow) and a large neuropathic ulcer on the midplantar surface. (B) Computed tomographic images (dorsoplantar and lateral views) of the patient’s right foot showing a subchondral cyst (arrow), fragmentation, disorganization, and loss of normal architecture of the talus, calcaneus, tarsal bones and bases of the metatarsals.
Neuropathic arthropathy, first described in 1868 by Jean-Martin Charcot,1 is an insidious, noninfective and progressive destruction of bones and joints, resulting in pathologic fractures, dislocations or subluxations that almost exclusively affects the foot and ankle. It is a complication of neuropathy and is most commonly caused by diabetes mellitus. Other less common causes include leprosy, alcohol abuse, multiple sclerosis and congenital neuropathy. In patients with diabetic neuropathy, the prevalence of the disorder ranges from 0.8% to 7.5%.2 Prevention of disease progression remains the mainstay of treatment, including prompt immobilization, absolute non–weight bearing and professional foot care on a regular basis.3 Surgery is usually reserved for patients with severe deformity or joint instability.4 Our patient declined surgical intervention in favour of conservative management.
Acknowledgement
The authors acknowledge Dr. Marco Cei for his expertise in this case.
Footnotes
-
Competing interests: None declared.
-
This article has been peer reviewed.