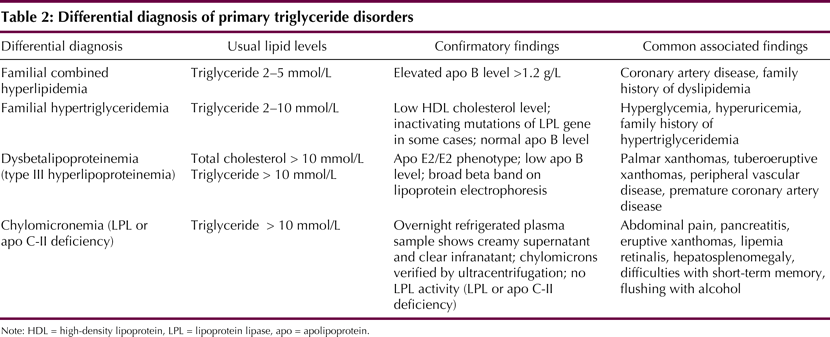
Article Figures & Tables
Figures
Fig. 1: Triglyceride pathway. The gut produces chylomicrons following the absorption of fat. The triglyceride (TG) component of chylomicrons is removed by lipoprotein lipase located on the vascular endothelium of muscle, myocardium and adipose tissue. The resulting chylomicron remnants are cleared from the circulation by hepatic receptors that recognize apolipoprotein E (apo E). The liver exports triglycerides into the circulation in the core of very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) particles. Photo: Paulette Dennis
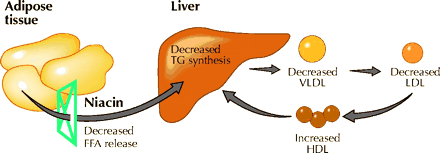
Fig. 2: Mechanism of niacin action. Niacin inhibits the release of free fatty acids from adipose tissue, which leads to decreased VLDL secretion by the liver. FFA = free fatty acids, TG = triglycerides, VLDL = very-low-density lipoprotein, LDL = low-density lipoprotein, HDL = high-density lipoprotein. Photo: Paulette Dennis