Article Figures & Tables
Figures
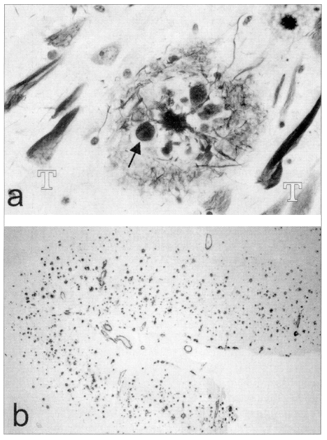
Fig. 1a: The main lesions of AD. Neurofibrillary tangles appear as flame-shaped dark structures (white T). A senile plaque, shown in centre, consists of a central core of amyloid surrounded by numerous distended neurites, one of which (arrow) clearly originates from a slender axon. (Silver stain; magnification × 400). Fig. 1b: Amyloid deposits in the form of senile plaques (appear as dots) occupy a significant fraction of the cerebal cortex, as shown here. (Stained with an antibody to β-amyloid; magnification × 20).
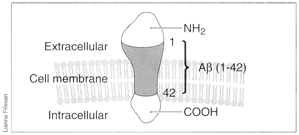
Fig. 2: Schematic showing amyloid precursor protein (APP) and the β-amyloid (Aβ) cleavage product.
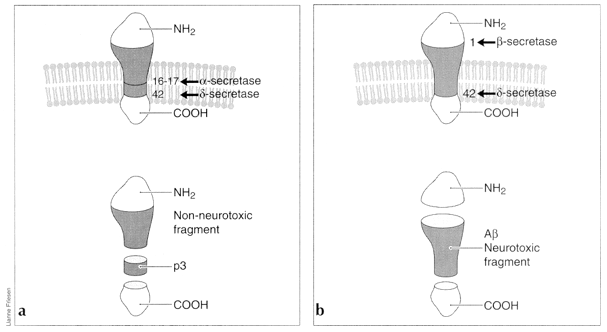
Fig. 3a: APP cleavage pathway via α-secretase. α-Secretase cleaves between residues 16 and 17, producing soluble, non-neurotoxic segments. Fig. 3b: APP cleavage pathway via β-secretase. This pathway produces the Aβ (1-42 fragment), which is putatively neurotoxic. This cleavage of the transmembrane region has been proposed to occur inside lysosomes (25) or in the trans-Golgi network during the secretory process. (26)
Fig. 4: Within the brain (represented by the circle) a neuron that has developed a tangle sends out 2 processes. One makes a synaptic contact, which is endangered as the tangle decreases the neuron's capacity to tend its branches. Another process is engulfed in an extracellular amyloid deposit, forming part of a senile plaque; an inflammatory cell (microglia) is in the vicinity. Factors influencing the development of AD appear outside the brain. The determinant genes influence the production of amyloid peptide, and the susceptibility gene (ApoE) is involved in the aggregation of amyloid and growth and repair functions of neurons. Age-related oxidative damage to neuronal membranes and proteins is enhanced by amyloid and inflammation; iron may participate in this process. Head trauma increases the development of plaques and tangles, whereas the mechanisms by which infarcts increase the risk for dementia in patients with AD lesions are unknown. Estrogen has multiple effects on the brain, several of which may influence the development of dementia.