Abstract
OBJECTIVE: To elucidate the effect of long-term weight variability on C-reactive protein (CRP) levels.
DESIGN: Cross-sectional study of the circulating CRP.
SUBJECTS: A total of 637 Japanese men aged 40–49 y in1997.
MEASUREMENTS: Serum CRP levels, body mass index in 1997 (current BMI), the slope of weight on age (weight-slope) representing an individual's weight trend of direction and magnitude, and the root mean square error around the slope of weight on age (weight-RMSE) representing the weight fluctuation magnitude, as calculated by a simple linear regression model in which each value of the subject's five actual weights (aged 20, 25, 30 y, five years ago, and current) was a dependent variable and the subject's ages independent variables.
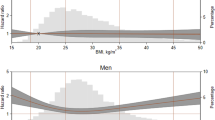
RESULTS: After adjustment for age and confounders, including smoking and health status, the odds ratios of elevated CRP (≥0.06 mg/dl) were 1.83 (95% CI: 1.25–2.69), 2.63 (1.69–4.11), and 10.31 (2.17–48.98) for upper normal-weight (BMI: 22–<25 kg/m2), overweight (25–<30), and obese (≥30) persons, respectively, compared with lower normal-weight persons (18.5–<22). Adjusting for age, confounders, and current BMI, weight-slope was positively associated with CRP level especially among subjects with BMI≥25 kg/m2 (trend P<0.01), and weight-RMSE was positively associated with CRP level particularly among subjects with BMI <25 kg/m2 (trend P<0.05).
CONCLUSION: Our results suggest a state of low-grade systemic inflammation not only in overweight and obese persons, but also in normal-weight persons with large weight fluctuation, possibly explaining in part the positive association between weight fluctuation and CVD.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kramer FM, Jeffery RW, Forster JL, Snell MK . Long-term follow-up of behavioral treatment for obesity: patterns of weight regain among men and women. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1989; 13: 123–136.
Iribarren C, Sharp DS, Burchfiel CM, Petrovitch H . Association of weight loss and weight fluctuation with mortality among Japanese American men. N Engl J Med 1995; 333: 686–692.
Lissner L, Odell PM, D'Agostino RB, Stokes III J, Kreger BE, Belanger AJ, Brownell KD . Variability of body weight and health outcomes in the Framingham population. N Engl J Med 1991; 324: 1839–1844.
Peters ET, Seidell JC, Menotti A, Arayanis C, Dontas A, Fidanza F, Karvonen M, Nedeljkovic S, Nissinen A, Buzina R . Changes in body weight in relation to mortality in 6441 European middle-aged men: the Seven Countries Study. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1995; 19: 862–868.
Hamm P, Shekelle RB, Stamler J . Large fluctuations in body weight during young adulthood and twenty-five-year risk of coronary death in men. Am J Epidemiol 1989; 129: 312–318.
Pepys MB . C-reactive protein fifty years on. Lancet 1981; 8221: 653–657.
Tracy RP, Lemaitre RN, Psaty BM, Ives DG, Evans RW, Cushman M, Meilahn EN, Kuller LH . Relationship of C-reactive protein to risk of cardiovascular disease in the elderly: results from the Cardiovascular Health Study and the Rural Health Promotion Project. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 1997; 17: 1121–1127.
Ridker PM, Cushman M, Stampfer MJ, Tracy RP, Hennekens CH . Inflammation, aspirin, and the risk of cardiovascular disease in apparently healthy men. N Engl J Med 1997; 336: 973–979.
Ridker PM, Cushman M, Stampfer MJ, Tracy RP, Hennekens CH . Plasma concentration of C-reactive protein and risk of developing peripheral vascular disease. Circulation 1998; 97: 425–428.
Ridker PM, Buring JE, Shih J, Matias M, Hennekens CH . Prospective study of C-reactive protein and the risk of future cardiovascular events among apparently healthy women. Circulation 1998; 98: 731–733.
Roivainen M, Viik-Kajander M, Palosuo T, Toivanen P, Leinonen M, Saikku P, Tenkanen L, Manninen V, Hovi T, Manttari M . Infections, inflammation, and the risk of coronary heart disease. Circulation 2000; 101: 252–257.
Koenig W, Sund M, Frohlich M, Fischer HG, Lowel H, Doring A, Hutchinson WL, Pepys MB . C-reactive protein, a sensitive marker of inflammation, predicts future risk of coronary heart disease in initially healthy middle-aged men: results from the MONICA (MONItoring trends and determinants in CArdiovascular disease) Augsberg Cohort Study, 1984 to 1992. Circulation 1999; 99: 237–242.
SPSS Incorporation. SPSS Base 10.0J user's guide. SPSS INC.: Chicago, IL; 1999.
Yoshiike N, Matsumura Y, Zaman MM, Yamaguchi M . Descriptive epidemiology of body mass index in Japanese adults in a representative sample from the National Nutrition Survey 1990–1994. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1998; 22: 684–687.
Trentham-Dietz A, Newcomb PA, Egan KM, Titus-Ernstoff L, Baron JA, Storer BE, Stampfer M, Willett WC . Weight change and risk of postmenopausal breast cancer (United States). Cancer Causes Control 2000; 11: 533–542.
Cassano PA, Rosner B, Vokonas PS, Weiss ST . Obesity and body fat distribution in relation to the incidence of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. A prospective cohort study of men in the normative aging study. Am J Epidemiol 1992; 136: 1474–1486.
Rimm EB, Stampfer MJ, Giovannucci E, Ascherio A, Spiegelman D, Colditz GA, Willett WC . Body size and fat distribution as predictors of coronary heart disease among middle-aged and older US men. Am J Epidemiol 1995; 141: 1117–1127.
Mendall MA, Patel P, Ballam L, Strachan D, Northfield TC . C reactive protein and its relation to cardiovascular risk factors: a population based cross sectional study. BMJ 1996; 312: 1061–1065.
Heilbronn LK, Noakes M, Clifton PM . Energy restriction and weight loss on very-low-fat diets reduce C-reactive protein concentrations in obese, healthy women. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2001; 21: 968–970.
Tchernof A, Nolan A, Sites CK, Ades PA, Poehlman ET . Weight loss reduces C-reactive protein levels in obese postmenopausal women. Circulation 2002; 105: 564–569.
Harris TB, Ballard-Barbasch R, Madans J, Makuc DM, Feldman JJ . Overweight, weight loss, and risk of coronary heart disease in older women. The NHANES I Epidemiologic Follow-up Study. Am J Epidemiol 1993; 137: 1318–1327.
Mohamed-Ali V, Pinkney JH, Coppack SW . Adipose tissue as an endocrine and paracrine organ. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1998; 22: 1145–1158.
Papanicolaou DA, Wilder RL, Manolagas SC, Chrousos GP . The pathophysiologic roles of interleukin-6 in human disease. Ann Intern Med 1998; 128: 127–137.
Pihl E, Jurimae T . Relationships between body weight change and cardiovascular disease risk factors in male former athletes. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2001; 25: 1057–1062.
Fried SK, Bunkin DA, Greenberg AS . Omental and subcutaneous adipose tissues of obese subjects release interleukin-6. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1998; 83: 847–850.
van der Kooy K, Leenen R, Seidell JC, Deurenberg P, Hautvast JG . Effect of a weight cycle on visceral fat accumulation.Am J Clin Nutr 1993; 58: 853–857.
Jebb SA, Goldberg GR, Coward WA, Murgatroyd PR, Prentice AM . Effects of weight cycling caused by intermittent dieting on metabolic rate and body composition in obese women. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1991; 15: 367–374.
Bhakdi S, Torzewski M, Klouche M, Hemmes M . Complement and atherogenesis: binding of CRP to degraded, nonoxidized LDL enhances complement activation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 1999; 19: 2348–2354.
Cermak J, Key NS, Bach RR, Balla J, Jacob HS, Vercellotti GM . C-reactive protein induces human peripheral blood monocytes to synthesize tissue factor. Blood 1993; 82: 513–520.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Dr Noboru Okamoto (Aichi San-no-maru Hospital), Dr Takashi Kawamura (Kyoto University Center for Student Health), and Dr Junji Toyama (Aichi Prefectural Owari Hospital) for their cooperation in conducting the survey and collecting information for this study.
This work is supported in part by a grant to Hideaki Toyoshima (09470112, 13470087), Koji Tamakoshi (12670352), and Hiroshi Yatsuya (13770192) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tamakoshi, K., Yatsuya, H., Kondo, T. et al. Long-term body weight variability is associated with elevated C-reactive protein independent of current body mass index among Japanese men. Int J Obes 27, 1059–1065 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0802386
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0802386
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Gender differences in midlife to later-life cumulative burden and variability of obesity measures and risk of all-cause and cause-specific mortality
International Journal of Obesity (2023)
-
Variability of adiposity indices and incident heart failure among adults with type 2 diabetes
Cardiovascular Diabetology (2022)
-
Adolescent overeating and binge eating behavior in relation to subsequent cardiometabolic risk outcomes: a prospective cohort study
Journal of Eating Disorders (2022)
-
BMI variability and incident diabetes mellitus, Tehran Lipid and Glucose Study (TLGS)
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Weight fluctuation, mortality, and cardiovascular disease in adults in 18 years of follow-up: Tehran Lipid and Glucose Study
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation (2022)