Abstract
Purpose
Reported sustained virological response (SVR) rates in Asians with chronic hepatitis C (CHC) exceed those of other ethnic groups, but differences in body weight across races potentially confound this observed superior response. Our aim was to determine whether Asian race independently predicts SVR within a multicultural clinic setting.
Methods
Patients with genotype 1, 2 and 3 CHC prescribed peginterferon and weight-based ribavirin were included in this retrospective study. Logistic regression was performed to identify factors associated with SVR.
Results
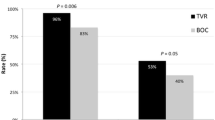
Three-hundred ninety-two patients (BMI 26.9 ± 5.0 kg/m2, genotype 1 66%, viral load 5.9 ± 0.66 log10 IU/ml, advanced fibrosis 53%) were included in this study. Caucasians comprised 81%, South Asians 9% and Asians (Non-South) 10%. SVR was achieved by 54% overall, but was highest amongst Asians (Non-South) (79%) compared with South Asians (56%, P = 0.04) and Caucasians (50%, P < 0.001) despite a predominance of genotype 3 infection amongst the South Asians. Asians (Non-South) had the highest SVR rate even amongst those infected with genotype 1 (75%) and those with advanced fibrosis (77%). Independent of viral genotype, Asian (Non-South) race was a strong predictor of SVR (OR 5.10 vs. Caucasians, 95% CI 1.72–17.71, OR 7.84 vs. South Asians, 95% CI 1.62–37.84), as were treatment naïve status (OR 3.85, 95% CI 1.76–8.89), non-diabetic status (OR 3.70, 95% CI 1.30–11.11), non-obesity (OR 2.13, 95% CI 1.06–4.35), peginterferon α2a (2.08 vs. α2b, 95% CI 1.16–3.85), steatosis <10% (OR 2.0, 95% CI 1.05–3.85) and ribavirin exposure (mg/kg/day) (OR 1.13, 95% CI 1.01–1.28).
Conclusion
Asian (Non-South) race is a strong independent predictor of SVR.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- CHC:
-
Chronic hepatitis C
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- HCV:
-
Hepatitis C virus
- IFN:
-
Interferon
- OR:
-
Odds ratio
- SVR:
-
Sustained virological response
References
Manns MP, McHutchison JG, Gordon SC, Rustgi VK, Shiffman M, Reindollar R, Goodman ZD, Koury K, Ling M, Albrecht JK. Peginterferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin compared with interferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin for initial treatment of chronic hepatitis C: a randomised trial. Lancet 2001;358:958–965
Fried MW, Shiffman ML, Reddy KR, Smith C, Marinos G, Goncales FL Jr, Haussinger D, Diago M, Carosi G, Dhumeaux D, Craxi A, Lin A, Hoffman J, Yu J. Peginterferon alfa-2a plus ribavirin for chronic hepatitis C virus infection. N Engl J Med 2002;347:975–982
Hadziyannis SJ, Sette H Jr, Morgan TR, Balan V, Diago M, Marcellin P, Ramadori G, Bodenheimer H Jr, Bernstein D, Rizzetto M, Zeuzem S, Pockros PJ, Lin A, Ackrill AM. Peginterferon-alpha2a and ribavirin combination therapy in chronic hepatitis C: a randomized study of treatment duration and ribavirin dose. Ann Intern Med 2004;140:346–355
Romero-Gomez M, Del Mar Viloria M, Andrade RJ, Salmeron J, Diago M, Fernandez-Rodriguez CM, Corpas R, Cruz M, Grande L, Vazquez L, Munoz-De-Rueda P, Lopez-Serrano P, Gila A, Gutierrez ML, Perez C, Ruiz-Extremera A, Suarez E, Castillo J. Insulin resistance impairs sustained response rate to peginterferon plus ribavirin in chronic hepatitis C patients. Gastroenterology 2005;128:636–641
Conjeevaram HS, Kleiner DE, Everhart JE, Hoofnagle JH, Zacks S, Afdhal NH, Wahed AS. Race, insulin resistance and hepatic steatosis in chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 2007;45:80–87
Chen L, Borozan I, Feld J, Sun J, Tannis LL, Coltescu C, Heathcote J, Edwards AM, McGilvray ID. Hepatic gene expression discriminates responders and nonresponders in treatment of chronic hepatitis C viral infection. Gastroenterology 2005;128:1437–1444
Ge D, Fellay J, Thompson AJ, Simon JS, Shianna KV, Urban TJ, Heinzen EL, Qiu P, Bertelsen AH, Muir AJ, Sulkowski M, McHutchison JG, Goldstein DB. Genetic variation in IL28B predicts hepatitis C treatment-induced viral clearance. Nature 2009;461:399–401
Suppiah V, Moldovan M, Ahlenstiel G, Berg T, Weltman M, Abate ML, Bassendine M, Spengler U, Dore GJ, Powell E, Riordan S, Sheridan D, Smedile A, Fragomeli V, Muller T, Bahlo M, Stewart GJ, Booth DR, George J. IL28B is associated with response to chronic hepatitis C interferon-alpha and ribavirin therapy. Nat Genet 2009;41:1100–1104
Tanaka Y, Nishida N, Sugiyama M, Kurosaki M, Matsuura K, Sakamoto N, Nakagawa M, Korenaga M, Hino K, Hige S, Ito Y, Mita E, Tanaka E, Mochida S, Murawaki Y, Honda M, Sakai A, Hiasa Y, Nishiguchi S, Koike A, Sakaida I, Imamura M, Ito K, Yano K, Masaki N, Sugauchi F, Izumi N, Tokunaga K, Mizokami M. Genome-wide association of IL28B with response to pegylated interferon-alpha and ribavirin therapy for chronic hepatitis C. Nat Genet 2009;41:1105–1109
Jacobson IM, Brown RS Jr, McCone J, Black M, Albert C, Dragutsky MS, Siddiqui FA, Hargrave T, Kwo PY, Lambiase L, Galler GW, Araya V, Freilich B, Harvey J, Griffel LH, Brass CA. Impact of weight-based ribavirin with peginterferon alfa-2b in African Americans with hepatitis C virus genotype 1. Hepatology 2007;46:982–990
Hepburn MJ, Hepburn LM, Cantu NS, Lapeer MG, Lawitz EJ. Differences in treatment outcome for hepatitis C among ethnic groups. Am J Med 2004;117:163–168
Freshwater DA, O’Donnell K, Mutimer DJ. Inferior response of Asian vs non-Asian hepatitis C genotype 3 infection to combination antiviral therapy. J Viral Hepat 2008;15:115–119
Yu ML, Dai CY, Huang JF, Chiu CF, Yang YH, Hou NJ, Lee LP, Hsieh MY, Lin ZY, Chen SC, Wang LY, Chang WY, Chuang WL. Rapid virological response and treatment duration for chronic hepatitis C genotype 1 patients: a randomized trial. Hepatology 2008;47:1884–1893
Yu ML, Dai CY, Huang JF, Hou NJ, Lee LP, Hsieh MY, Chiu CF, Lin ZY, Chen SC, Wang LY, Chang WY, Chuang WL. A randomised study of peginterferon and ribavirin for 16 versus 24 weeks in patients with genotype 2 chronic hepatitis C. Gut 2007;56:553–559
Missiha S, Heathcote J, Arenovich T, Khan K. Impact of Asian race on response to combination therapy with peginterferon alfa-2a and ribavirin in chronic hepatitis C. Am J Gastroenterol 2007;102:2181–2188
Bressler BL, Guindi M, Tomlinson G, Heathcote J. High body mass index is an independent risk factor for nonresponse to antiviral treatment in chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 2003;38:639–644
Reddy KR, Shiffman ML, Morgan TR, Zeuzem S, Hadziyannis S, Hamzeh FM, Wright TL, Fried M. Impact of ribavirin dose reductions in hepatitis C virus genotype 1 patients completing peginterferon alfa-2a/ribavirin treatment. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2007;5:124–129
Ferenci P, Laferl H, Scherzer TM, Gschwantler M, Maieron A, Brunner H, Stauber R, Bischof M, Bauer B, Datz C, Loschenberger K, Formann E, Staufer K, Steindl-Munda P. Peginterferon alfa-2a and ribavirin for 24 weeks in hepatitis C type 1 and 4 patients with rapid virological response. Gastroenterology 2008;135:451–458
Yu ML, Dai CY, Chen SC, Chiu CC, Lee LP, Lin ZY, Hsieh MY, Wang LY, Chuang WL, Chang WY. Human leukocyte antigen class I and II alleles and response to interferon-alpha treatment, in Taiwanese patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection. J Infect Dis 2003;188:62–65
Dai CY, Chuang WL, Chang WY, Chen SC, Lee LP, Hsieh MY, Hou NJ, Lin ZY, Huang JF, Wang LY, Yu ML. Tumor necrosis factor- alpha promoter polymorphism at position -308 predicts response to combination therapy in hepatitis C virus infection. J Infect Dis 2006;193:98–101
Persico M, Capasso M, Russo R, Persico E, Croce L, Tiribelli C, Iolascon A. Elevated expression and polymorphisms of SOCS3 influence patient response to antiviral therapy in chronic hepatitis C. Gut 2008;57:507–515
Walsh MJ, Jonsson JR, Richardson MM, Lipka GM, Purdie DM, Clouston AD, Powell EE. Non-response to antiviral therapy is associated with obesity and increased hepatic expression of suppressor of cytokine signalling 3 (SOCS-3) in patients with chronic hepatitis C, viral genotype 1. Gut 2006;55:529–535
WHO. Obesity: preventing and managing a global epidemic. Report on a WHO Consultation in Obesity, Geneva 3–5 June, 1997. WHO/NUT/NCD/98.1. Technical Report Series Number 894. Volume WHO/NUT/NCD/98.1. Technical Report Series Number 894. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2000
WHO Expert Consultation. Appropriate body-mass index for Asian populations and its implications for policy and intervention strategies. Lancet 2004;363:157–163
Powis J, Peltekian KM, Lee SS, Sherman M, Bain VG, Cooper C, Krajden M, Deschenes M, Balshaw RF, Heathcote EJ, Yoshida EM. Exploring differences in response to treatment with peginterferon alpha 2a (40kD) and ribavirin in chronic hepatitis C between genotypes 2 and 3. J Viral Hepat 2008;15:52–57
Yu ML, Chuang WL, Chen SC, Dai CY, Hou C, Wang JH, Lu SN, Huang JF, Lin ZY, Hsieh MY, Tsai JF, Wang LY, Chang WY. Changing prevalence of hepatitis C virus genotypes: molecular epidemiology and clinical implications in the hepatitis C virus hyperendemic areas and a tertiary referral center in Taiwan. J Med Virol 2001;65:58–65
Yamada G, Iino S, Okuno T, Omata M, Kiyosawa K, Kumada H, Hayashi N, Sakai T. Virological response in patients with hepatitis C virus genotype 1b and a high viral load: impact of peginterferon-alpha-2a plus ribavirin dose reductions and host-related factors. Clin Drug Investig 2008;28:9–16
Fung J, Lai CL, Hung I, Young J, Cheng C, Wong D, Yuen MF. Chronic hepatitis C virus genotype 6 infection: response to pegylated interferon and ribavirin. J Infect Dis 2008;198:808–812
Noppornpanth S, Sablon E, De Nys K, Truong XL, Brouwer J, Van Brussel M, Smits SL, Poovorawan Y, Osterhaus AD, Haagmans BL. Genotyping hepatitis C viruses from Southeast Asia by a novel line probe assay that simultaneously detects core and 5′ untranslated regions. J Clin Microbiol 2006;44:3969–3974
Vutien P, Nguyen NH, Trinh HN, Li J, Garcia RT, Garcia G, Nguyen KK, Nguyen HA, Levitt BS, Keeffe EB, Nguyen MH. Similar treatment response to peginterferon and ribavirin in Asian and Caucasian patients with chronic hepatitis C. Am J Gastroenterol 2010;105:1110–1115
McNeely MJ, Boyko EJ. Type 2 diabetes prevalence in Asian Americans: results of a national health survey. Diabetes Care 2004;27:66–69
McHutchison JG, Lawitz EJ, Shiffman ML, Muir AJ, Galler GW, McCone J, Nyberg LM, Lee WM, Ghalib RH, Schiff ER, Galati JS, Bacon BR, Davis MN, Mukhopadhyay P, Koury K, Noviello S, Pedicone LD, Brass CA, Albrecht JK, Sulkowski MS. Peginterferon alfa-2b or alfa-2a with ribavirin for treatment of hepatitis C infection. N Engl J Med 2009;361:580–593
Rumi MG, Aghemo A, Prati GM, D’Ambrosio R, Donato MF, Soffredini R, Del Ninno E, Russo A, Colombo M. Randomized study of peginterferon-alpha2a plus ribavirin vs peginterferon-alpha2b plus ribavirin in chronic hepatitis C. Gastroenterology 2010;138:108–115
Ascione A, De Luca M, Tartaglione MT, Lampasi F, Di Costanzo GG, Lanza AG, Picciotto FP, Marino-Marsilia G, Fontanella L, Leandro G. Peginterferon alfa-2a plus ribavirin is more effective than peginterferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin for treating chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Gastroenterology 2010;138:116–122
Awad T, Thorlund K, Hauser G, Stimac D, Mabrouk M, Gluud C. Peginterferon alpha-2a is associated with higher sustained virological response than peginterferon alfa-2b in chronic hepatitis C: systematic review of randomized trials. Hepatology 2010;51:1176–1184
Hsu CS, Liu CH, Liu CJ, Chen CL, Lai MY, Chen PJ, Chen DS, Kao JH. Factors affecting early viral load decline of Asian chronic hepatitis C patients receiving pegylated interferon plus ribavirin therapy. Antivir Ther 2009;14:45–54
Pattullo V, Ravindran NC, Mazzulli T, Wong DK, Heathcote EJ. Pegylated interferon plus optimized weight-based ribavirin dosing negate the influence of weight and body mass index on early viral kinetics and sustained virological response in chronic hepatitis C. J Viral Hepat 2010. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2893.2010.01248.x
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to acknowledge Tamara Arenovich and Chris Meaney for performing the statistical analysis.
Conflict of interest
VP received scholarship funding from the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia and the University Health Network, Toronto, Canada. EJH has received grant support from the following: Axcan Pharma, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squib, Debio Pharma, Gilead Sciences, GlaxoSmithKline, Hoffman-LaRoche, Human Genome Sciences, Intercept Pharm, Merck, Tibotec, Vertex. EJH has acted as consultant for Axcan Pharma, Gilead Sciences, Hoffman-LaRoche, Merck, Tibotec. JH has acted as speaker for Axcan Pharma, Gilead Sciences, Hoffman-LaRoche, Merck, Tibotec. DKHW has no disclosures.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pattullo, V., Heathcote, E.J. & Wong, D.K.H. Superior response to pegylated interferon and ribavirin in Asians with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatol Int 4, 723–731 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-010-9207-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-010-9207-1