Abstract
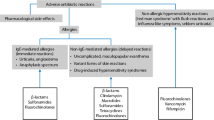
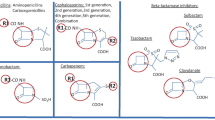
Antibiotics are among the most widely and heavily prescribed drugs, but despite this, allergic reactions to most groups of antibiotics are relatively uncommon—especially when compared with the number and frequency of type 1 hypersensitivity responses to the β-lactams (ie, penicillins, cephalosporins, and, to a lesser extent, carbopenems). Still, there remains a steady flow of reports of allergic reactions to some topically used antibiotics (eg, rifamycin SV and bacitracin). Moreover, aminoglycosides (eg, neomycin and gramicidin) may be implicated more often than previously suspected. Despite advances in our understanding of the structural basis of the allergenicity of β-lactam antibiotics, the insights have not readily transferred into routine use to improve diagnoses of reactions to individual penicillins and cephalosporins. This remains a challenge in drug allergy, as does the need for further chemical, immunologic, and clinical research on cephalosporin breakdown products and the so-called multiple antibiotic allergy syndrome.
Similar content being viewed by others
References and Recommended Reading
Baldo BA, Zhao Z, Pham NH: Structural determinants of antibiotic allergy. Curr Allergy Rep 2001, 1:23–31.
Tilles SA, Slatore CG: Hypersensitivity reactions to non-β-lactam antibiotics. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 2003, 24:221–228.
Hassaballa H, Mallick N, Orlowski J: Vancomycin anaphylaxis in a patient with vancomycin-induced red man syndrome. Am J Ther 2000, 7:319–320.
Hwu J-J, Chen K-H, Hsu W-M, et al.: Ocular hypersensitivity to topical vancomycin in a case of chronic endophthalmitis. Cornea 2005, 24:754–756.
Asero R: Teicoplanin-induced anaphylaxis. Allergy 2006, 61:1370–1372.
Erel F, Karaayvaz M, Deveci M, et al.: Severe anaphylaxis from rifamycin SV. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 1998, 81:257–260.
Magnan A, Venemalm L, Porri F, et al.: Anaphylactic reaction to rifamycin SV: presence of specific IgE antibodies. J Allergy Clin Immunol 1999, 103:954–956.
Ebo DG, Verheecke G, Bridts CH, et al.: Perioperative anaphylaxis from locally applied rifamycin SV and latex. Brit J Anaesth 2006, 96:738–741.
Antevil JL, Muldoon MP, Battaglia M, et al.: Intraoperative anaphylactic shock associated with bacitracin irrigation during revision total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg 2003, 85A:339–342.
Schalock PC, Zug KA: Bacitracin. Cutis 2005, 76:105–107.
Yung MW, Rajendra T: Delayed hypersensitivity reaction to topical aminoglycosides in patients undergoing middle ear surgery. Clin Otolaryngol 2002, 27:365–368.
Harle DG, Baldo BA: Identification of penicillin allergenic determinants that bind IgE antibodies in the sera of subjects with penicillin allergy. Mol Immunol 1990, 27:1063–1071.
Baldo BA, Pham NH: Structure-activity studies on drug induced anaphylactic reactions. Chem Res Toxicol 1994, 7:703–721.
Pham NH, Baldo BA: β-Lactam drug allergens: fine structural recognition patterns of cephalosporin-reactive IgE antibodies. J Mol Recognit 1996, 9:287–296.
Blanca M, Mayorga C, Sanchez F, et al.: Differences in serum IgE antibody activity to benzylpenicillin and amoxicillin measured by RAST in a group of penicillin allergic patients. Allergy 1991, 46:632–638.
Baldo BA, Pham NH, Weiner J: Detection and side-chain specificity of IgE antibodies to flucloxacillin in allergic subjects. J Mol Recognit 1995, 8:171–177.
Baldo BA: Penicillins and cephalosporins as allergens: structural aspects of recognition and cross-reactions. Clin Exp Allergy 1999, 29:744–749.
Baldo BA: Diagnosis of allergy to penicillins and cephalosporins. Stuctural and immunochemical considerations. Allergy Clin Immunol Int 2000, 12:206–212.
Torres MJ, Blanca M, Fernandez J, et al.: Diagnosis of immediate allergic reactions to beta-lactam antibiotics. Allergy 2003, 58:961–972.
Bousquet PJ, Co-Minh HB, Arnoux B, et al.: Importance of mixture of minor determinants and benzylpenicilloyl poly-L-lysine skin testing in the diagnosis of β-lactam allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2005, 115:1314–1316.
Matheu V, Perez-Rodriguez E, Sanchez-Machin I, et al.: Major and minor determinants are high performance skin tests in β-lactam allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2005, 116:1167–1168.
Zhao Z, Baldo BA, Baumgart KW, et al.: Fine structural recognition specificities of IgE antibodies distinguishing amoxicilloyl and amoxicillanyl determinants in allergic subjects. J Mol Recognit 2001, 14:300–307.
Zhao Z, Batley M, D’Ambrosio C, et al.: In vitro reactivity of penicilloyl and penicillanyl albumin and polylysine conjugates with IgE-antibody. J Immunol Methods 2000, 242:43–51.
Hamilton-Miller JMT, Newton GGF, Abraham EP: Products of aminolysis and enzymic hydrolysis of the cephalosporins. Biochem J 1970, 116:371–384.
Hamilton-Miller JMT, Richards E, Abraham EP: Changes in proton-magnetic-resonance spectra during aminolysis and enzymic hydrolysis of cephalosporins. Biochem J 1970, 116:385–395.
Bundgaard H: Chemical studies related to cephalosporin allergy. I. Kinetics of aminolysis of cephalosporins and effect of C-3 substituents on β-lactam reactivity. Archiv for Pharmaci og Chemi 1975, 5:94–123.
Harle DG, Baldo BA: Drugs as allergens: An immunoassay for detecting IgE antibodies to cephalosporins. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol 1990, 92:439–444.
Zhao Z, Baldo BA, Rimmer J: β-Lactam allergenic determinants: fine structural recognition of a cross-reacting determinant on benzylpenicillin and cephalothin. Clin Exp Allergy 2002, 32:1644–1650.
Romano A, Gueant-Rodriguez RM, Viola M, et al.: Diagnosing immediate allergic reactions to cephalosporins. Clin Exp Allergy 2005, 35:1234–1242.
Antunez C, Blanca-Lopez N, Torres MJ, et al.: Immediate allergic reactions to cephalosporins: evaluation of cross-reactivity with a panel of penicillins and cephalosporins. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2006, 117:404–410.
Kim S-H, Choi J-H, Park H-S: Heterogeneity of the IgE response to allergenic determinants of cefaclor in serum samples from patients with cefaclor-induced anaphylaxis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 2005, 94:700–704.
Sanchez-Sancho F, Perez-Inestrosa E, Suau R, et al.: Synthesis, characterization and immunochemical evaluation of cephalosporin antigenic determinants. J Mol Recognit 2003, 16:148–156.
Blanca-Gomez M, Torres MJ, Mayorga C, et al.: Immediate allergic reactions to betalactams: facts and controversies. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol 2004, 4:261–266.
Rodriguez-Pena R, Antunez C, Martin E, et al.: Allergic reactions to β-lactams. Expert Opin Drug Saf 2006, 5:31–48.
Park H-S, Kim K-U, Lee Y-M, et al.: Occupational asthma and IgE sensitization to 7-aminocephalosporanic acid. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2004, 113:785–787.
Orhan F, Odemis E, Yaris N, et al.: A case of IgE-mediated hypersensitivity to cefepime. Allergy 2004, 59:239–241.
Poston SA, Jennings HR, Poe KL: Cefazolin tolerance does not predict ceftriaxone hypersensitivity: unique side chains precipitate anaphylaxis. Pharmacotherapy 2004, 24:668–672.
Pichichero ME: A review of evidence supporting the American Academy of Pediatrics recommendation for prescribing cephalosporin antibiotics for penicillin-allergic patients. Pediatrics 2005, 115:1048–1057.
Romano A, Viola M, Gueant-Rodriguez R-M, et al.: Selective immediate hypersensitivity to cefodizime. Allergy 2005, 60:1545–1546.
Thethi AK, Van Dellen RG: Dilemmas and controversies in penicillin allergy. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am 2004, 24:445–461.
Cunha BA: Antibiotic selection in the penicillin-allergic patient. Med Clin N Amer 2006, 90:1257–1264.
Solensky R: Drug hypersensitivity. Med Clin North Am 2006, 90:233–260.
Prescott Jr WA, De Pestel DD, Ellis JJ, et al.: Incidence of carbapenem-associated allergic-type reactions among patients with versus patients without a reported penicillin allergy. Clin Infect Dis 2004, 38:1102–1107.
Saxon A, Adelman DC, Patel A, et al.: Imipenem cross-reactivity with penicillin in humans. J Allergy Clin Immunol 1988, 82:213–217.
McConnell SA, Penzac SR, Warmack TS, et al.: Incidence of imipenem hypersensitivity reactions in febrile neutropenic bone marrow transplant patients with a history of penicillin allergy. Clin Infect Dis 2000, 31:1512–1514.
Sodhi M, Axtell SS, Callahan J, et al.: Is it safe to use carbapenems in patients with a history of allergy to penicillin? J Antimicrob Chemother 2004, 54:1155–1157.
Romano A, Viola M, Gueant-Rodriguez R-M, et al.: Brief communication: Tolerability of menopenem in patients with IgE-mediated hypersensitivity to penicillins. Ann Intern Med 2007, 146:266–269.
Macy E: Multiple antibiotic allergy syndrome. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am 2004, 24:533–543.
Pham NH, Baldo BA, Puy RM: Studies on the mechanism of multiple drug allergies. Structural basis of drug recognition. J Immunoassay Immunochem 2001, 22:47–73.
Turvey SE, Cronin B, Arnold AD, et al.: Antibiotic desensitization for the allergic patient: 5 years of experience and practice. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 2004, 92:426–432.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baldo, B.A., Zhao, Z. & Pham, N.H. Antibiotic allergy: Immunochemical and clinical considerations. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep 8, 49–55 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11882-008-0010-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11882-008-0010-1