Abstract
Purpose
To study the long-term effect of being overweight on mortality in very elderly subjects.
Methods
The medical records of 470 inpatients (226 males) with a mean age of 81.5 ± 7 years and hospitalized in an acute geriatric ward between 1999 and 2000 were reviewed for this study. Body mass index (BMI) at admission day was subdivided into quartiles: <22, 22–25, 25.01–28, and ≥28 kg/m2. Patients were followed-up until August 31, 2004. Mortality data were taken from death certificates.
Results
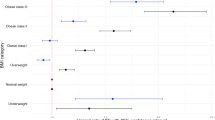
During a mean follow-up of 3.46 ± 1.87 years (median 4.2 years [range 1.6 to 5.34 years]), 248 patients died. Those who died had lower baseline BMI than those who survived (24.1 ± 4.2 vs 26.3 ± 4.6 kg/m2; p < .0001). The age-adjusted mortality rate decreased from 24 to 9.6 per 100 patient-years from the highest to lowest BMI quartile (p < .001). BMI was associated with all-cause and cause-specific mortality even after controlling for sex. A multivariate Cox proportional hazards model identified that even after controlling for male gender, age, renal failure, and diabetes mellitus, which increased the risk of all-cause mortality, elevated BMI decreased the all-cause mortality risk.
Conclusions
In very elderly subjects, elevated BMI was associated with reduced mortality risk.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BMI:
-
body mass index
- BP:
-
blood pressure
- mmHg:
-
millimeter Hg (mercury)
- mg/dL:
-
milligram/deciliter
- Kg:
-
kilogram
- cm:
-
centimeter
- m2 :
-
meter square
- SD:
-
standard deviation
- IHD:
-
ischemic heart disease
- CHF:
-
congestive heart failure
- HR:
-
hazard ratios
- CI:
-
confidence intervals
- PH:
-
proportional hazards
- EHF = Ĥ 0(t):
-
empirical cumulative hazards function
- vs:
-
versus
- WC:
-
waist circumference
- SBP:
-
systolic blood pressure
- DBP:
-
diastolic blood pressure
- ACE:
-
angiotensin converting enzyme
- M/F:
-
males/females
- beats/min:
-
beats per minute
References
Manson JE, Willett WC, Stampfer MJ, Colditz GA, Hunter DJ, Hankinson SE, et al. Body weight and mortality among women. N Engl J Med. 1995;333(11):677–85.
Must A, Spadano J, Coakley EH, Field AE, Colditz G, Dietz WH. The disease burden associated with overweight and obesity. JAMA. 1999;282(16):1523–9.
Sullivan DH, Johnson LE. Nutrition and aging. In: Hazzard WR, Blass JP, Halter JB, Ouslander JG, Tinetti ME, eds. Principles of Geriatric Medicine and Gerontology. 5 ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2003:265–83.
Calle EE, Rodriguez C, Walker-Thurmond K, Thun MJ. Overweight, obesity, and mortality from cancer in a prospectively studied cohort of U.S. adults. N Engl J Med. 2003;348(17):1625–38.
Calle EE, Thun MJ, Petrelli JM, Rodriguez C, Heath CW Jr. Body-mass index and mortality in a prospective cohort of U.S. adults. N Engl J Med. 1999;341(15):1097–105.
Kopelman PG. Obesity as a medical problem. Nature. 2000;404(6778):635–43.
Willett WC, Manson JE, Stampfer MJ, Colditz GA, Rosner B, Speizer FE, et al. Weight, weight change, and coronary heart disease in women. Risk within the ‘normal’ weight range. JAMA. 1995;273(6):461–5.
Curtis JP, Selter JG, Wang Y, Rathore SS, Jovin IS, Jadbabaie F, et al. The obesity paradox: body mass index and outcomes in patients with heart failure. Arch Intern Med. 2005;165(1):55–61.
Escalante A, Haas RW, del Rincon I. Paradoxical effect of body mass index on survival in rheumatoid arthritis: role of comorbidity and systemic inflammation. Arch Intern Med. 2005;165(14):1624–9.
Gustafsson F, Kragelund CB, Torp-Pedersen C, et al. Effect of obesity and being overweight on long-term mortality in congestive heart failure: influence of left ventricular systolic function. Eur Heart J. 2005;26(1):58–64.
Kalantar-Zadeh K, Block G, Horwich T, Fonarow GC. Reverse epidemiology of conventional cardiovascular risk factors in patients with chronic heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;43(8):1439–44.
Kalantar-Zadeh K, Block G, Humphreys MH, Kopple JD. Reverse epidemiology of cardiovascular risk factors in maintenance dialysis patients. Kidney Int. 2003;63(3):793–808.
Romero-Corral A, Montori VM, Somers VK, et al. Association of bodyweight with total mortality and with cardiovascular events in coronary artery disease: a systematic review of cohort studies. Lancet. 2006;368(9536):666–78.
Chang-Claude J, Hermann S, Eilber U, Steindorf K. Lifestyle determinants and mortality in German vegetarians and health-conscious persons: results of a 21-year follow-up. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2005;14(4):963–8.
Hayashi R, Iwasaki M, Otani T, et al. Body mass index and mortality in a middle-aged Japanese cohort. J Epidemiol. 2005;15(3):70–7.
Hu G, Tuomilehto J, Silventoinen K, et al. The effects of physical activity and body mass index on cardiovascular, cancer and all-cause mortality among 47 212 middle-aged Finnish men and women. Int J Obes. 2005;29(8):894–902.
Stevens J, Cai J, Pamuk ER, et al. The effect of age on the association between body-mass index and mortality. N Engl J Med. 1998;338(1):1–7.
Landi F, Onder G, Gambassi G, et al. Body mass index and mortality among hospitalized patients. Arch Intern Med. 2000;160(17):2641–4.
Weiss A, Grossman E, Beloosesky Y, Grinblat J. Orthostatic hypotension in acute geriatric ward: is it a consistent finding? Arch Intern Med. 2002;162(20):2369–74.
Jagoe RT, Goodship TH, Gibson GJ. The influence of nutritional status on complications after operations for lung cancer. Ann Thorac Surg. 2001;71:766–8.
Nicoletti I, Cicoira M, Morando G, et al. Impact of body mass index on short-term outcome after acute myocardial infarction: does excess body weight have a paradoxical protective role? Int J Cardiol. 2006;107(3):395–9.
Allison DB, Zhu SK, Plankey M, et al. Differential associations of body mass index and adiposity with all-cause mortality among men in the first and second National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (NHANES I and NHANES II) follow-up studies. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2002;26(3):410–6.
Heitmann BL, Erikson H, Ellsinger BM, et al. Mortality associated with body fat, fat-free mass and body mass index among 60-year-old swedish men—a 22-year follow-up. The study of men born in 1913. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2000;24(1):33–7.
Fonarow GC, Srikanthan P, Costanzo MR, Cintron GB, Lopatin M, ADHERE Scientific Advisory Committee and Investigators. An obesity paradox in acute heart failure: analysis of body mass index and inhospital mortality for 108,927 patients in the Acute Decompensated Heart Failure National Registry. Am Heart J. 2007;153:74–81.
Horwich TB, Fonarow GC. The impact of obesity on survival in patients with heart failure. Heart Fail Monit. 2002;3:8–14.
Flegal KM, Graubard BI, Williamson DF, Gail MH. Excess deaths associated with underweight, overweight, and obesity. JAMA. 2005;293(15):1861–7.
Schooling CM, Lam TH, Li ZB, et al. Obesity, physical activity, and mortality in a prospective Chinese elderly cohort. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166(14):1498–504.
Willett WC, Dietz WH, Colditz GA. Guidelines for healthy weight. N Engl J Med. 1999;341(6):427–34.
Wilson PW, D’Agostino RB, Sullivan L, et al. Overweight and obesity as determinants of cardiovascular risk: the Framingham experience. Arch Intern Med. 2002;162(16):1867–72.
Adams KF, Schatzkin A, Harris TB, et al. Overweight, obesity, and mortality in a large prospective cohort of persons 50 to 71 years old. N Engl J Med. 2006;355(8):763–78.
Jee SH, Sull JW, Park J, et al. Body-mass index and mortality in Korean men and women. N Engl J Med. 2006;355(8):779–87.
Lindsted KD, Singh PN. Body mass and 26 y risk of mortality among men who never smoked: a re-analysis among men from the Adventist Mortality Study. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 1998;22(6):544–8.
Stevens J, Plankey MW, Williamson DF, et al. The body mass index–mortality relationship in white and African American women. Obes Res. 1998;6(4):268–77.
Zamboni M, Mazzali G, Zoico E, et al. Health consequences of obesity in the elderly: a review of four unresolved questions. Int J Obes. 2005;29(9):1011–29.
Heiat A, Vaccarino V, Krumholz HM. An evidence-based assessment of federal guidelines for overweight and obesity as they apply to elderly persons. Arch Intern Med. 2001;161(9):1194–203.
Hu FB, Willett WC, Li T, et al. Adiposity as compared with physical activity in predicting mortality among women. N Engl J Med. 2004;351(26):2694–703.
Inoue K, Shono T, Toyokawa S, Kawakami M. Body mass index as a predictor of mortality in community-dwelling seniors. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2006;18(3):205–10.
Janssen I, Katzmarzyk PT, Ross R. Body mass index is inversely related to mortality in older people after adjustment for waist circumference. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2005;53(12):2112–38.
Shah B, Sucher K, Hollenbeck CB. Comparison of ideal body weight equations and published height–weight tables with body mass index tables for healthy adults in the United States. Nutr Clin Pract. 2006;21:312–9.
Price GM, Uauy R, Breeze E, Bulpitt CJ, Fletcher AE. Weight, shape, and mortality risk in older persons: elevated waist–hip ratio, not high body mass index, is associated with a greater risk of death. Am J Clin Nutr. 2006;84(2):449–60.
Wolfe M, Nolte KB, Yoon SS. Fatal infectious disease surveillance and the medical examiner database. Emerg Infect Dis. 2004;10:48–53.
Conflict of Interest Statement
None of the authors of this manuscript has any conflict of interest regarding funding source or other potential source of support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weiss, A., Beloosesky, Y., Boaz, M. et al. Body Mass Index is Inversely Related to Mortality in Elderly Subjects. J GEN INTERN MED 23, 19–24 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11606-007-0429-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11606-007-0429-4